Documentation
- Pharmaceutical Guideline

- Dec 24, 2020
- 3 min read
Updated: Sep 11, 2022
You might have read so many guidelines and articles on Documentation, in this article, I am not going to explain the same things here.
This article is not on good documentation practice (GDP)
this article is not covering data integrity
In this article, I am going to explain basic things on the documentation which are applicable anywhere.
In this article, We will understand the following terminology which will be useful in the entire learning journey
Basically, this article is published for conceptual clarity
What is Documentation?
What is the difference between Documents and records?
Structure of Documentation
Importance of The Documentation
What is Documentation?
The Documentation is a combination of Document, Record, Its generation, archival, and destruction (Lifecycle)
What is the difference between Documents and records?
Documents:
Present
Current
Can be revised
Explaining What to do
Explaining How to do
Instruction
Records:
Past
Permanent
Cannot be changed
Explaining What have been done
Explaining How it has been done
Evidence
Compare carefully point to point for better clarity
Structure of Documentation
The Documentation structure is explained by the Documentation pyramid.
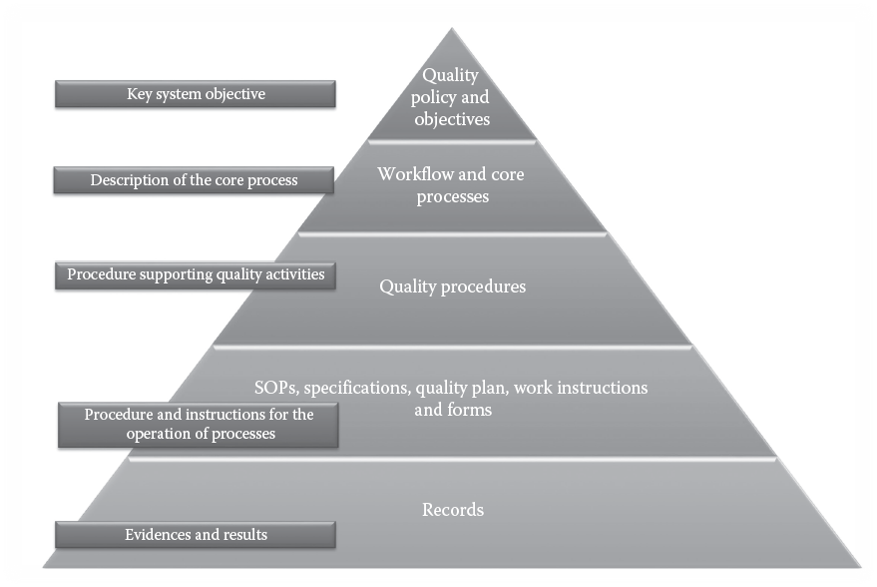
This pyramid of the documentation describes the operational flow of documented information in the organization and represents the levels for the types of documents that are usually used in a Quality Management System (QMS), from the planning of strategic stages to the daily work of performing activities and filling out forms. This method clearly illustrates that with each descending level of the pyramid, the amount of required documented information will increase. This kind of pyramid provides navigation for users throughout the various documentations in the organization. In other words, when an interested party (internal like a user or an employee or external like an auditor) needs to get familiarize with the documentation of the organization, they can use this structure for orientation.
Level-1 Documentation
Strategic Level
These documentations are called Policy documents;
In the first level of the documentation pyramid, we will find documentation of declarative statements by the organization that includes the key elements of the QMS, and that will set the strategic direction of the QMS. This documented information has a clear goal: to introduce and communicate the intentions, scope, and structure of the QMS in the organization. It includes elements such as QMS scope, quality policies, quality objectives or references to them, organizational structure, exclusions, the general process of the organization, etc.
Example: Quality Policy, Quality Manual, Site Master File (SMF), Validation Master Plan (VMP)
Level-2 Documentation
Workflow and Core Processes
Workflow describes the work process of an organizational unit (an organization or a part of the organization) where each step depends on the preceding step. It depicts the business activity with step processes, their resources, their sequences (progression), and interactions that transform inputs into outputs, for example, materials into goods or information into services. Workflow can appear as a diagram or as a description (text).
Example: Master Formula Record, Organogram, Department manual
Level-3 Documentation
Procedures or Process Diagrams to Support Quality Activities
On this level, you may include procedures or instructions that support quality activities that the standard describes and demands, The documentation which is required to maintain the Quality Management system shall include in this level
Maintenance of documented information
Control of nonconforming product
Internal audit
Corrective action
Risk Management
QMS SOP / Protocols
Level-4 Documentation
Quality Plan, SOPs, Specifications, Process Diagrams, Procedures, Work Instructions, and Forms
This type of documented information, which belongs to the fourth level in our pyramid, has the goal of supporting operations of processes and directing and instructing personnel on how to perform activities. This type of documented information has the objectives of
Supporting the workflow in the organization
Defining the required information and data needed to perform activities and operate processes
Describing the responsibilities and authorities of people and/or organizational functions regarding processes and activities
Ensuring effective planning, operations, and control activities during the realization of the product
Describing activities needed to support the workflow
Describing the interrelations of processes or activities
Describing methods for monitoring and measurement activities
Describing the expected evidence and records
Communicating information regarding processes and activities
Assisting in training
Reducing mistakes
Level-5 Documentation
Records
Every activity is generating the records, results, evidence, or proofs, it is very important to maintain as per its lifecycle.
The record shall be archive in such a way so it can be retrieved within the stipulated time.
Example: Executed forms, Executed Batch records, Validation / Qualification Reports...
Importance of The Documentation
Remember, If you want to sale you are the product in any country, first of all, you have to clear the registration process --- This requires Documentation
During Audit; the Auditor is auditing three following things;
The Procedure (SOP) --- this is Document
The practice which they observe during the audit, which must be matched with your SOP--- The SOP is Document
The Auditor verifies evidence for the activity which is not performed in front of them--- this is records
So you can understand the importance of documentation
To update yourself; regularly visit our website: www.pharmaceuticalguideline.com and become a member (it's FREE) by clicking the Login button at the top right corner of the webpage, also subscribe to our newsletter, Like our website, follow us on
Telegram, Download Telegram App on your Mobile and use @pharmaceuticalguideline for search.









Documentation is a vital part of any creative or production process, helping ensure consistency, transparency, and quality. Whether you're crafting detailed design notes or tracking materials used, proper documentation supports better decision-making. This is especially true in the fashion and accessories industry where every detail matters. For example, when producing genuine leather handbags, clear documentation of sourcing, craftsmanship, and care instructions adds value and builds customer trust.